Invention Summary:
Recently deep neural networks have been successfully applied in channel coding to improve the decoding performance. However, the state-of-the-art neural channel decoders cannot achieve high decoding performance and low complexity simultaneously.
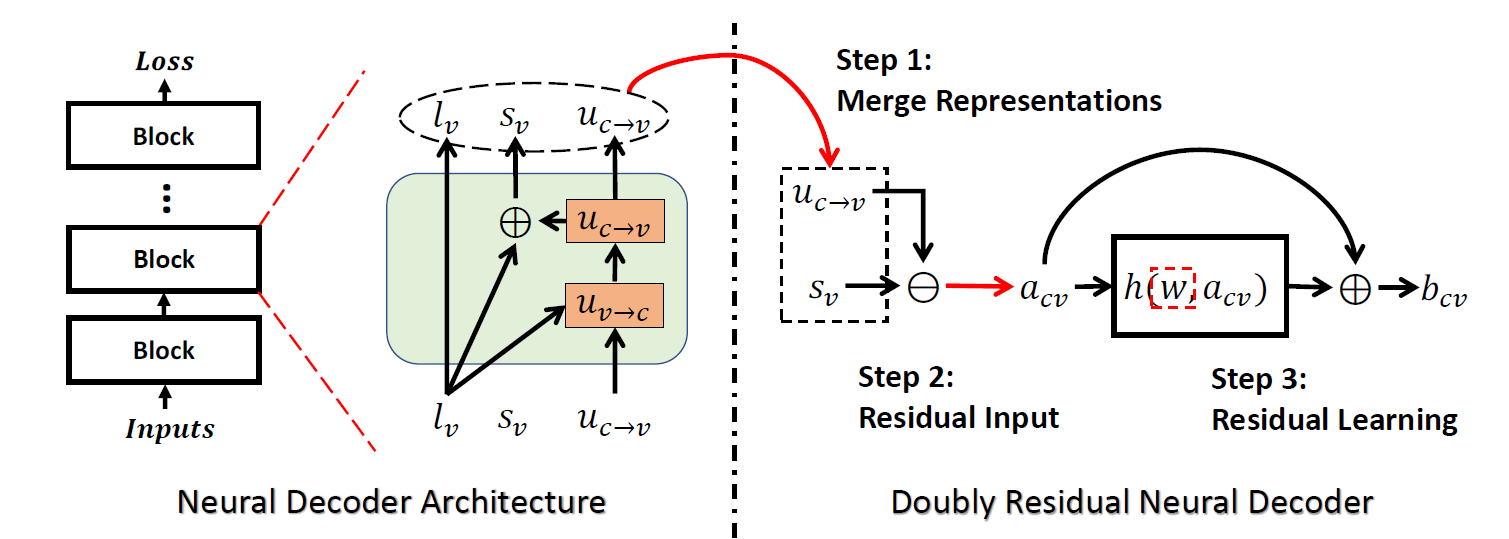
To overcome this challenge, Rutgers researcher have developed a novel doubly residual neural (DRN) decoder. By integrating both the residual input and residual learning to the design of neural channel decoder, DRN enables significant decoding performance improvement while maintaining low complexity.
Extensive experiment results show that on different types of channel codes, the DRN decoder consistently outperform the state-of-the-art decoders in terms of decoding performance, model sizes and computational cost.
Advantages:
- Achieve similar or better bit error rate (BER) performance as existing methods at substantially lower cost
- Decrease required model size by 23-100X
- Reduce computational cost by up to 75%
Market Applications:
- Communication and computer storage system for a better error-correcting performance
Intellectual Property & Development Status: Patent Pending. Available for licensing and/or research collaboration.
Publication: Siyu Liao, Chunhua Deng, Miao Yin, and Bo Yuan. " Doubly Residual Neural Decoder: Towards Low-Complexity High-Performance Channel Decoding." 2102.03959.pdf (arxiv.org) (2021)