ANIMAL MODEL FOR MALIGNANT MELANOMA AND USES THEREOF
Invention Summary:
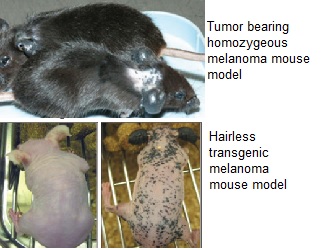
Advances in translational research are very closely linked to the rational design and selection of animal models. Patients with advanced melanoma have very low 5-year survival rates of 1%-2% and there is a critical need for clinically relevant discoveries and development of therapeutic treatment approaches. Metabotropic Glutamate receptor-1 (Grm1) has been implicated in the development of melanocytic neoplasms. Therefore developing inhibitors/antagonists against Grm1 could potentially arrest the progression of this pathway. Scientists at Rutgers have developed a novel melanoma animal model that expresses Grm1 in a melanocyte-specific manner and as a result, exhibits a predisposition to the development of melanoma. This technology will advance testing of new chemotherapeutic agents as well as conducting melanoma research. In summary, this technology fills the gap in the availability of effective model systems to provide insights into molecular derangements, assess drug efficacies and optimize treatments associated with melanoma.
Market Applications:
- Melanoma Research
- Melanoma Detection
- Cancer Therapies
- Animal Models for Cancer
Advantages:
- Melanoma Research
- Melanoma Detection
- Cancer Therapies
- Animal Models for Cancer
- Discovery of novel therapeutic agents that antagonize Grm1
- Screening technology for potential drug candidates for the prevention/treatment of melanoma
Intellectual Property & Development Status:
Issued patent US 7,385,103 - Animal model, and treatment for malignant melanoma.
Select Publications:
- Teh, Jessica L. F., and Suzie Chen. 2012. Glutamatergic signaling in cellular transformation. Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research 25 (3): 331-42.
- Baljinnyam, Erdene, Masanari Umemura, Mariana De Lorenzo, Lai-Hua Xie, Martha Nowycky, Mizuka Iwatsubo, Suzie Chen, James Goydos, and Kousaku Iwatsubo. 2011. Gbetagamma subunits inhibit epac-induced melanoma cell migration. BMC Cancer 11 (1): 256.
- Pollock, P. M., K. Cohen-Solal, R. Sood, J. Namkoong, J. J. Martino, A. Koganti, H. Zhu, C. Robbins, I. Makalowska, and S. S. Shin. 2003. Melanoma mouse model implicates metabotropic glutamate signaling in melanocytic neoplasia. Nature Genetics 34 (1): 108-12.
Patent Information:
| Title |
App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |
Patent Status |
|
|
|
ID: 2003-167
Category:
Inventors:
Keywords:
|